1.
How is food transported in plants? ,Or What is translocation? Elaborate.
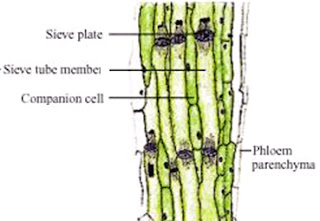 Transporation of soluble products of photosynthesis is called translocation
and it occurs in the part of vascular tissue known as Phloem. Besides this phloem
also transport amino acids and other substances. These substances are
especially delivered to the storage organs of roots, fruits and seed and to
growing organs. Phloem transports food materials from the leaves to different
parts of the plant body. Unlike Xylem it transport material in both direction. The
transportation of food in phloem is achieved by using energy from ATP. As a
result, the osmotic pressure in the tissue increases causing water to move into
it. This pressure moves the material in the phloem to the tissues which have
less pressure. This is helpful in moving materials according to the needs of
the plant. For example, the food material, such as sucrose, is transported into
the phloem tissue using ATP energy. The translocation of food and other
substances takes place in sieve tubes with the help of adjacent companion cells
in both direction
Transporation of soluble products of photosynthesis is called translocation
and it occurs in the part of vascular tissue known as Phloem. Besides this phloem
also transport amino acids and other substances. These substances are
especially delivered to the storage organs of roots, fruits and seed and to
growing organs. Phloem transports food materials from the leaves to different
parts of the plant body. Unlike Xylem it transport material in both direction. The
transportation of food in phloem is achieved by using energy from ATP. As a
result, the osmotic pressure in the tissue increases causing water to move into
it. This pressure moves the material in the phloem to the tissues which have
less pressure. This is helpful in moving materials according to the needs of
the plant. For example, the food material, such as sucrose, is transported into
the phloem tissue using ATP energy. The translocation of food and other
substances takes place in sieve tubes with the help of adjacent companion cells
in both direction
2.
Write the methods used by the plants to
get rid of excretory products.
Plants get rid of:
1. water by transpiration.
2. waste products may store in vacuoles or may be stored in leaves which
fall off.
3.resine and gums are stored in xylem.
4.some waste substance may be excreted in the soil.
5. as by products move out of the plants by diffusion through stomata.
3.
How is lymph formed? Write its functions.
Through the pores present in the walls of capillaries, some amount of
plasma, proteins and blood cells escape into intercellular spaces in the
tissues to form the tissue fluid or lymph. From intercellular spaces, it enters
into lymphatic capillaries, which join to form lymph vessels, which open into
larger veins. Lymph carries digested and
4.
How do the alveoli of lungs in human body
help in the exchange of gases?
Alveoli provides a surface for the exchange of gases.An extensive
network of blood vessels is present in the wall of the alveoli. By lifting our
ribs and flatten the diaphragm, the chest cavity becomes spacious. Air is
sucked into the lungs and alveoli.The oxygen from the breath, diffuses into the
blood and CO2 from the blood brought from the body, diffuses out into the air.
No comments:
Post a Comment